Near visual acuity of high myopes after cataract surgery: a real-world analysis
关键词
摘要
全文
INTRODUCTION
Numerous studies have demonstrated that near vision is just as important as distance vision for overall visual function and quality of life.[10-12] Unaided near tasks, such as self-care and the use of digital devices, represent the primary visual function needs of individuals, especially those with low vision.[13] Highly myopic cataract patients are accustomed to seeing near objects without correction,[14, 15] and therefore, a myopic postoperative target refraction is generally preferred for them, as opposed to targeting emmetropia in normal cataract patients. However, there is currently no consensus on the level of myopia to target, nor on whether astigmatism correction should be fully considered for highly myopic cataract patients who require distance glasses after cataract surgery. Previous studies have primarily focused on the distance visual acuity of high myopic patients after cataract surgery, [16, 17] but the distribution of near visual acuity in this population remains largely unknown.
The aim of the present study was to evaluate the distribution of near visual acuity and the related postoperative refractive outcomes in highly myopic patients who underwent monofocal IOL implantation. This assessment was based on real-world data sourced from the largest tertiary eye hospital in China, aiming to provide insights for optimizing surgical planning for this patient group in clinical practice.
METHODS
Study population
Questionnaire and examination
Data management
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Demographic and clinical characteristics
Table 1 Demographic and clinical characteristics of participants
|
Distribution |
|
|
Age (years) |
|
|
≤ 50 |
112 (16.87) |
|
50 - 60 |
201 (30.27) |
|
60 - 70 |
183 (27.56) |
|
≥ 70 |
168 (25.30) |
|
Sex |
|
|
Male |
301 (45.33) |
|
Female |
363 (54.67) |
|
Diabetes |
53 (7.98) |
|
Hypertension |
154 (23.19) |
|
Overweight/Obesity |
|
|
Yes |
196 (29.52) |
|
No |
459 (69.13) |
|
Missing |
9 (1.36) |
|
Highest education |
|
|
< 10 years |
127 (19.13) |
|
High school |
167 (25.15) |
|
University or higher |
263 (39.61) |
|
Missing |
107 (16.11) |
|
Axial length (mm) |
|
|
26 to 28 |
277 (41.72) |
|
28 to 30 |
173 (26.05) |
|
≥ 30 |
214 (32.23) |
|
Postoperative best-corrected visual acuity |
|
|
≥ 20/40 |
518 (78.01) |
|
20/40 to 20/200 |
119 (17.92) |
|
< 20/200 |
27 (4.07) |
|
Postoperative spherical equivalent (D) |
|
|
≥ -0.5 |
56 (8.43) |
|
-1.5 to -0.5 |
47 (7.08) |
|
-2.5 to -1.5 |
207 (31.17) |
|
-3.5 to -2.5 |
271 (40.81) |
|
< -3.5 |
83 (12.50) |
|
Postoperative astigmatism (D) |
|
|
≥ -1 |
453 (68.22) |
|
-2 to -1 |
163 (24.55) |
|
< -2 |
48 (7.23) |
|
Type of astigmatism |
|
|
Against-the-rule |
466 (70.18) |
|
Oblique |
53 (7.98) |
|
With-the-rule |
145 (21.84) |
Data were presented as frequency along with the corresponding percentage.
The distribution of UCNVA
Figure 1 Density distribution and marginal histograms of uncorrected near visual acuity and parameters including axial length (A), postoperative best-corrected visual acuity (B), and postoperative spherical equivalent (C).
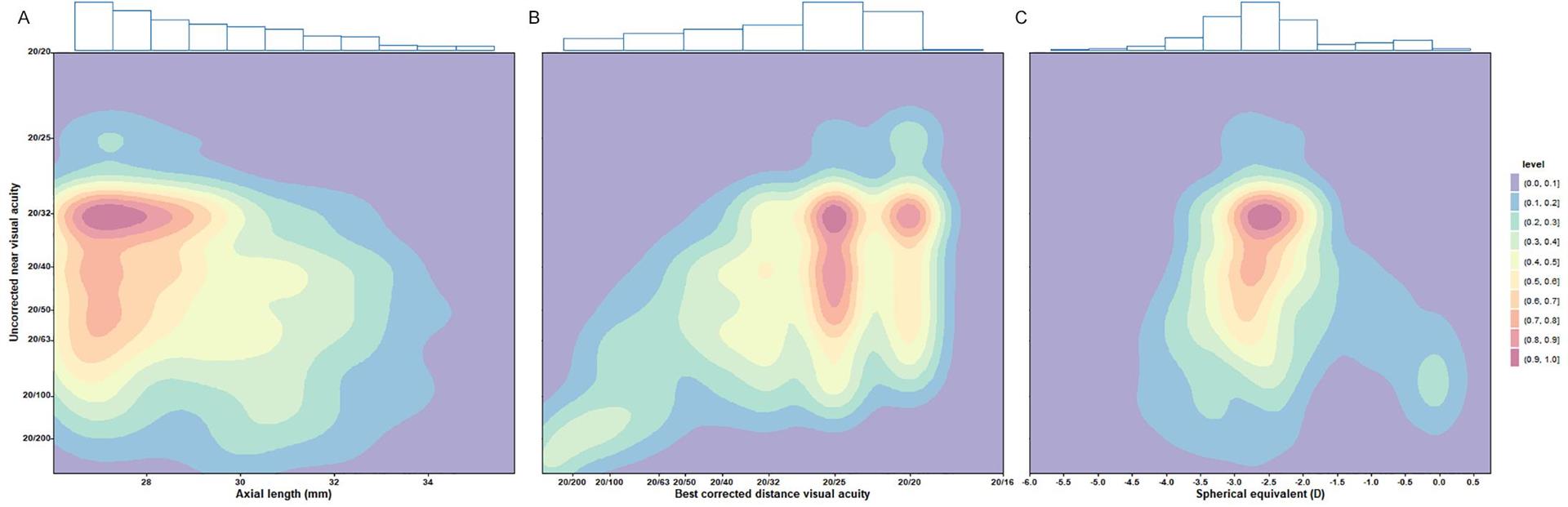
Table 2 Uncorrected near visual acuity of highly myopic eyes after cataract surgery
|
Uncorrected near visual acuity |
P value |
|||||
|
≥ 20/40 |
20/40-20/60 |
20/60-20/200 |
20/200-20/400 |
< 20/400 |
||
|
Age (years) |
|
|
|
|
|
0.10 |
|
≤ 50 |
53 (47.32) |
24 (21.43) |
32 (28.57) |
3 (2.68) |
0 (0) |
|
|
50 - 60 |
109 (54.23) |
36 (17.91) |
50 (24.88) |
3 (1.49) |
3 (1.49) |
|
|
60 - 70 |
84 (45.90) |
28 (15.30) |
66 (36.07) |
3 (1.64) |
2 (1.09) |
|
|
≥ 70 |
73 (43.45) |
19 (11.31) |
69 (41.07) |
4 (2.38) |
3 (1.79) |
|
|
Sex |
|
|
|
|
|
0.54 |
|
Male |
154 (51.16) |
42 (13.95) |
96 (31.89) |
5 (1.66) |
4 (1.33) |
|
|
Female |
165 (45.45) |
65 (17.91) |
121 (33.33) |
8 (2.20) |
4 (1.10) |
|
|
Diabetes |
|
|
|
|
|
0.95 |
|
Yes |
23 (43.40) |
9 (16.98) |
19 (35.85) |
1 (1.89) |
1 (1.89) |
|
|
No |
296 (48.45) |
98 (16.04) |
198 (32.41) |
12 (1.96) |
7 (1.15) |
|
|
Hypertension |
|
|
|
|
|
0.39 |
|
Yes |
74 (48.05) |
22 (14.29) |
52 (33.77) |
2 (1.30) |
4 (2.60) |
|
|
No |
245 (48.04) |
85 (16.67) |
165 (32.35) |
11 (2.16) |
4 (0.78) |
|
|
Overweight/Obesity |
|
|
|
|
|
0.98 |
|
Yes |
96 (48.98) |
32 (16.33) |
61 (31.12) |
4 (2.04) |
3 (1.53) |
|
|
No |
218 (47.49) |
75 (16.34) |
152 (33.12) |
9 (1.96) |
5 (1.09) |
|
|
Highest education |
|
|
|
|
|
0.006a |
|
< 10 years |
49 (38.58) |
14 (11.02) |
56 (44.09) |
5 (3.94) |
3 (2.36) |
|
|
High school |
84 (50.30) |
30 (17.96) |
49 (29.34) |
2 (1.20) |
2 (1.20) |
|
|
University or higher |
149 (56.65) |
37 (14.07) |
71 (27.00) |
3 (1.14) |
3 (1.14) |
|
|
Axial length (mm) |
|
|
|
|
|
<0.001a |
|
26 to 28 |
145 (52.35) |
45 (16.25) |
84 (30.32) |
3 (1.08) |
0 (0) |
|
|
28 to 30 |
98 (56.65) |
21 (12.14) |
47 (27.17) |
3 (1.73) |
4 (2.31) |
|
|
≥ 30 |
76 (35.51) |
41 (19.16) |
86 (40.19) |
7 (3.27) |
4 (1.87) |
|
|
Postoperative best-corrected visual acuity |
< 0.001a |
|||||
|
≥ 20/40 |
293 (56.56) |
88 (16.99) |
137 (26.45) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
|
20/40 to 20/200 |
26 (21.85) |
18 (15.13) |
72 (60.50) |
3 (2.52) |
0 (0) |
|
|
< 20/200 |
0 (0) |
1 (3.70) |
8 (29.63) |
10 (37.04) |
8 (29.63) |
|
|
Postoperative spherical equivalent (D) |
< 0.001a |
|||||
|
≥ -0.5 |
5 (8.93) |
6 (10.71) |
41 (73.21) |
0 (0) |
4 (7.14) |
|
|
-1.5 to -0.5 |
13(27.66) |
14 (29.79) |
18 (38.30) |
2 (4.26) |
0 (0) |
|
|
-2.5 to -1.5 |
132 (63.77) |
24 (11.59) |
48 (23.19) |
2 (0.97) |
1 (0.48) |
|
|
-3.5 to -2.5 |
153 (56.46) |
46 (16.97) |
65 (23.99) |
5 (1.85) |
2 (0.74) |
|
|
< -3.5 |
16 (19.28) |
17 (20.48) |
45 (54.22) |
4 (4.82) |
1 (1.20) |
|
|
Postoperative astigmatism (D) |
< 0.001a |
|||||
|
≥ -1 |
248 (54.75) |
70 (15.45) |
125 (27.59) |
3 (0.66) |
7 (1.55) |
|
|
-2 to -1 |
58 (35.58) |
31 (19.02) |
64 (39.26) |
9 (5.52) |
1 (0.61) |
|
|
< -2 |
13 (27.08) |
6 (12.50) |
28 (58.33) |
1 (2.08) |
0 (0) |
|
|
Type of astigmatism |
|
|
|
|
|
0.44 |
|
Against-the-rule |
222 (47.64) |
80 (17.17) |
149 (31.97) |
9 (1.93) |
6 (1.29) |
|
|
Oblique |
29 (54.72) |
7 (13.21) |
14 (26.42) |
1 (1.89) |
2 (3.77) |
|
|
With-the-rule |
68 (46.90) |
20 (13.79) |
54 (37.24) |
3 (2.07) |
0 (0) |
|
a. Statistically significant (P <0.05).
Data were presented as frequency along with the corresponding percentage.
The associated factors of UCNVA less than 20/40
Figure 2 Bubble plot and marginal density curves showing the distribution of postoperative spherical equivalent and astigmatism in eyes with and without near visual impairment (< 20/40)
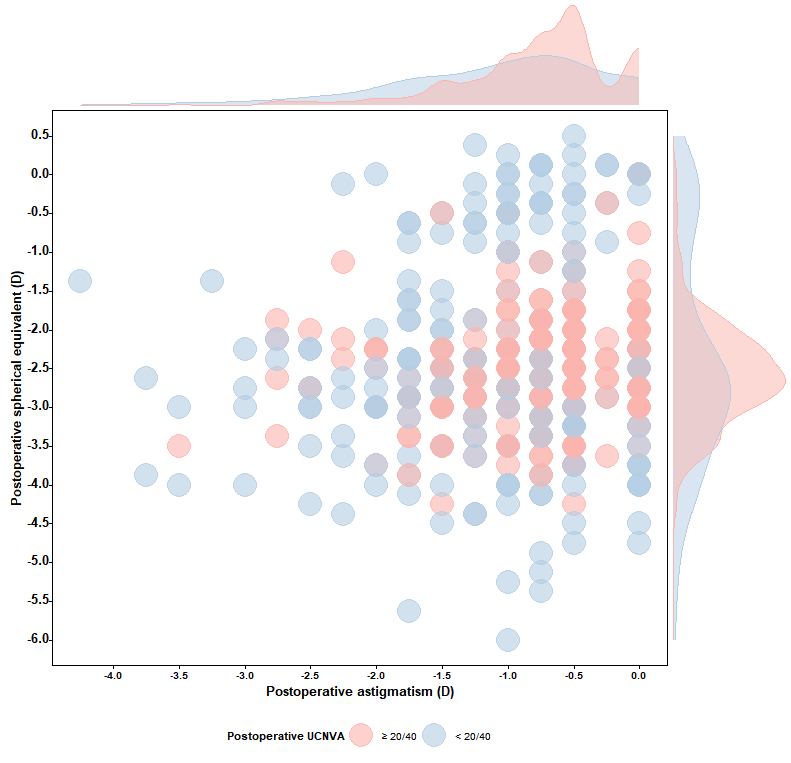
UCNVA = uncorrected near visual acuity.
Table 3 Multiple logistic regression of near vision impairment in highly myopic eyes after cataract surgery
|
OR (95% CI) |
P value |
|
|
Highest education |
|
|
|
< 10 years |
Ref |
- |
|
High school |
0.85 (0.48, 1.50) |
0.57 |
|
University or higher |
0.69 (0.41, 1.18) |
0.17 |
|
Axial length (mm) |
|
|
|
26 to 28 |
Ref |
- |
|
28 to 30 |
0.79 (0.48, 1.31) |
0.37 |
|
≥ 30 |
1.35 (0.83, 2.19) |
0.23 |
|
Postoperative best-corrected visual acuity |
|
|
|
≥ 20/40 |
Ref |
- |
|
< 20/40 |
5.44 (3.14, 9.42) |
< 0.001a |
|
Postoperative spherical equivalent (D) |
|
|
|
-2.5 |
Refb |
- |
|
> -0.5 |
19.73 (4.88, 79.68) |
< 0.001a |
|
-1 to -0.5 |
13.19 (2.52, 68.94) |
0.002a |
|
-1.5 to -1 |
4.96 (1.37, 18.03) |
0.015a |
|
-2 to -1.5 |
1.18 (0.45, 3.11) |
0.74 |
|
-2.5 to -2 |
0.74 (0.32, 1.70) |
0.48 |
|
-3 to -2.5 |
0.83 (0.38, 1.80) |
0.64 |
|
-3.5 to -3 |
1.73 (0.75, 4.01) |
0.20 |
|
-4 to -3.5 |
4.17 (1.56, 11.14) |
0.004a |
|
< -4 |
8.51 (2.31, 31.32) |
0.001a |
|
Postoperative astigmatism (D) |
|
|
|
≥ -1 |
Ref |
- |
|
-2 to -1 |
2.00 (1.24, 3.22) |
0.004a |
|
< -2 |
4.27 (1.88, 9.66) |
0.001a |
OR: odds ratio; CI: confidence interval.
Adjusted for age and sex.
a.Statistically significant (P <0.05).
b.The spherical equivalent of -2.5 D was set as the reference, corresponding to a theoretical focal length of 40 cm.